Thrombocytosis: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Thrombocytosis is a disease of the bone marrow and blood that affects about two to three in 100,000 people. Most cases are in women over the age of 50 years. Learn more about the different types of the disease, symptoms, causes and treatment here.
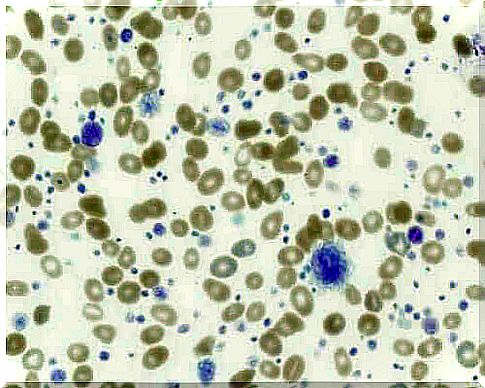
Thrombocytosis is a disease characterized by a dramatic increase in the number of platelets in the blood. The normal number of platelets in the blood is between 150,000 and 450,000 for every microliter of blood. If the number is slightly higher or slightly lower, it is still considered normal. But if the number is much higher, then the person suffers from thrombocytosis
Platelets are produced in the bone marrow from cells called megakaryocytes. They are kind of fragments of blood devoid of nucleus and irregular shape. They play an important role in blood clotting, which is necessary to stop bleeding.
In short, thrombocytosis is a disease of the bone marrow and blood. This disease is also known under the name of thrombocythemia or under the name of hyperplateletosis. Too many platelets in the body can lead to serious health problems such as a heart attack or cardiovascular accident, among others.
Types of thrombocytosis
Roughly speaking , there are two types of thrombocytosis: primary or essential thrombocytosis and secondary thrombocytosis. In primary thrombocytosis, the bone marrow produces platelets abnormallyfor some unknown reason. For its part, secondary thrombocytosis is the consequence of other diseases such as infection, cancer, anemia …
Thrombocytosis can also be classified into three groups: congenital, acquired and pseudothrombocytosis. Congenital thrombocytosis is linked to the hereditary factor and is present at birth.
As for acquired thrombocytosis, it is divided into two groups:
- Primary Thrombocytosis: Primary thrombocytosis is essential thrombocytosis and is defined as myeloproliferative neoplasia caused by genetic mutations. In many cases, the root cause of the disease is unknown
- Secondary thrombocytosis : this thrombocytosis is the consequence of other diseases. It concerns 85% of cases. More than half of these cases are due to infection
Pseudothrombocytosis, for its part, corresponds to cases of false positives. Certain circumstances cause certain cytoplasmic fragments to be mistaken for platelets, giving rise to an erroneous diagnosis.
Symptoms
In most cases, the disease has no symptoms. It is usually detected accidentally after a blood count. When the disease is primary or essential, the patient may have a few symptoms such as headache, nausea, chest pain, loss of vision, or visualization of spots.
Fatigue, night sweats, and weight loss are other common symptoms. Clinical suspicion is stronger if, in addition, the patient has a history of early abortions in the first trimester of pregnancy, splenomegaly or enlargement of the spleen, bleeding and hypertension.
It is also very common for a patient with essential thrombocytosis to have erythromelalgia. It is a vasodilation of the arteries in the hand and feet, which causes an increase in temperature in the extremities as well as itching, pain and erythema.
Causes of thrombocytosis

Everything indicates that essential thrombocytosis is caused by an acquired somatic mutation, that is, not inherited. In 50% of cases, a mutation of the JAK2 genes is observed. In many other cases, a mutation of the CARL gene is observed. There have also been cases of mutations in the MPL, THPO and TET2 genes.
Several of these genes are responsible for making proteins, which have a decisive influence on the division of blood cells and, in particular, of platelets. The mutation is thought to cause the symptoms of essential thrombocytosis, but it is not yet clear how this process takes place.
In very many cases, no mutation is detected. Therefore, it is completely unknown what can be the cause behind the primary form of the disease. As for the secondary type, it is due to a basic disease as already mentioned previously.
The treatment
Essential thrombocytosis does not require treatment, provided the patient’s condition remains stable and the patient has no signs or symptoms of the disease. Your doctor may recommend that you take aspirin every day to prevent blood clots from forming.
If the patient has a history of or is at risk for cardiovascular disease, the doctor is most likely to prescribe medication to reduce the number of platelets. This is also advisable if the patient is over sixty years of age or the platelet count is over one million.
If the form of the disease is secondary, treatment is simply to control the disease causing the thrombocytosis. Thrombocytapheresis or plaqueopheresis should only be used in an emergency. This process consists of a filtration of the blood similar to a dialysis.