All About Joints
Joints allow limbs to move in all directions. They also provide mechanical support to the bone structure. In the human body, there are 205 bones connected to at least one other bone.
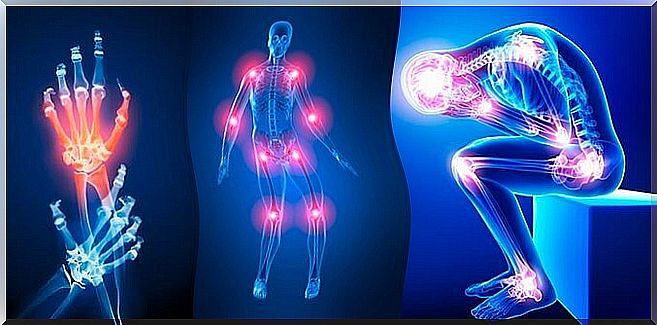
In the human body, there are 205 bones connected to at least one other bone. This connection is possible thanks to the joints, which guarantee a smooth and fluid physiological movement.
Depending on their location in the human body, the joints provide stability and movement.
How do the joints work?
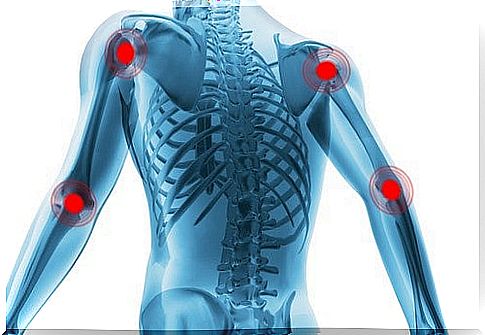
To better understand how they work, we will divide them by their level of movement.
Reduced or no mobility
Non-mobile joints are more stable. They firmly join the bones together, so that the possible movement is zero or almost zero.
For example, those located in the skull are attached to fibrous tissue that prevents movement of adjacent bones. In this way, they protect the brain.
Reduced movement
Fibrous connective tissue allows bones to bind together, and in this case, with very little movement. Its main function is to support the weight of the body in order to provide it with support and stability.
For example, the tibia and fibula are bones with limited space between them and which provide stability to the upright body.
The joints of the spine allow reduced movements which, when working together, give the body the flexibility needed to acquire different postures.
With a large range of motion
These joints do not directly bind the bones together. There is a lubricating fluid that envelops the joint surface and allows mobility.
Joints with a large range of motion are less stable. Most of them are located in the part of the skeleton that forms the extremities of the body (arms, legs, hands and feet) or appendicular skeleton. Its function makes muscular action on the bones possible.
Ligaments and cartilage
A ligament is a structure made up of fibrous tissue that serves to bind and stabilize the bones in the joints.
Ligaments connect adjacent bones in a joint. Thus, they allow and facilitate the movement which delimits the natural anatomical directions. Thus, they limit abnormalities and prevent injuries.
Cartilage provides movement between the bones. It acts as a shock absorber that prevents contact of one bone with another.
The cartilage is wrapped around the joint capsule, reinforced by ligaments. These (the cartilage and ligaments) work together to bind the bones in the joints.
To be able to talk about joint food supplements, it is essential to first understand the importance of joints for the human body.
Without them there would be no movement and the human body would be physically inflexible. Cartilage and ligaments are also closely related to the joints.
Wear
Activities that produce a strong impact on the joint cause the constant work of this system and, as a result, the wear and tear of cartilages and ligaments.
The cartilage is the part that suffers the most from wear and tear: it breaks down, becomes thinner and thinner, which ends up causing an annoying pain caused by the rubbing of the bones. In extreme cases, it can even happen to prevent the flexibility of the joint.
You don’t have to wait for pain to appear before realizing the importance of joint health and its effects on daily life.
However, wear and tear is preventable and is reduced through healthy lifestyles. Controlling your weight, exercising and eating a balanced diet are certainly helpful tips. If you really want to recover the joint structure, you have to provide it with nutrients.
Supplements to maintain joint health
Glucosamine
One of the best supplements out there for treating joints is glucosamine. Our body already produces this natural component, which is found around the joints supporting the cartilage.
As we age, glucosamine levels decrease and cause the joint to gradually break down. For this reason, it is important to ingest it.
- It can be obtained from shellfish, such as crab or lobster.
- It is also available in food supplements sold in health food stores.
Chondroitin
Chondroitin sulfate is made up of a chain of alternative sugars that help build and repair cartilage.
Chondroitin is usually extracted from animal cartilage.
MSM
MSM, or methyl sulfonylmethane, is a natural source of sulfur with important properties that strengthen and maintain joint tissue.
Good joint health is fundamental to our overall well-being. Incorporate these supplements into your diet and enjoy a better quality of life.